window.alert()
window.alert() instructs the browser to display a dialog with an optional message, and to wait until the user dismisses the dialog.
Under some conditions — for example, when the user switches tabs — the browser may not actually display a dialog, or may not wait for the user to dismiss the dialog.
<script>
window.alert("Hello world!");
alert("Hello world!");
</script>Both produce:

The alert dialog should be used for messages which do not require any response on the part of the user, other than the acknowledgement of the message.
Dialog boxes are modal windows - they prevent the user from accessing the rest of the program's interface until the dialog box is closed. For this reason, you should not overuse any function that creates a dialog box (or modal window).
window.prompt()
window.prompt() instructs the browser to display a dialog with an optional message prompting the user to input some text, and to wait until the user either submits the text or cancels the dialog.
Under some conditions — for example, when the user switches tabs — the browser may not actually display a dialog, or may not wait for the user to submit text or to cancel the dialog.
<script>
let sign = prompt("What's your sign?");
if (sign.toLowerCase() === "scorpio") {
alert("Wow! I'm a Scorpio too!");
}
// there are many ways to use the prompt feature
sign = window.prompt(); // open the blank prompt window
sign = prompt(); // open the blank prompt window
sign = window.prompt("Are you feeling lucky"); // open the window with Text "Are you feeling lucky"
sign = window.prompt("Are you feeling lucky", "sure"); // open the window with Text "Are you feeling lucky" &s default value "sure"
</script>When the user clicks the OK button, text entered in the input field is returned. If the user clicks OK without entering any text, an empty string is returned. If the user clicks the Cancel button, this function returns null.
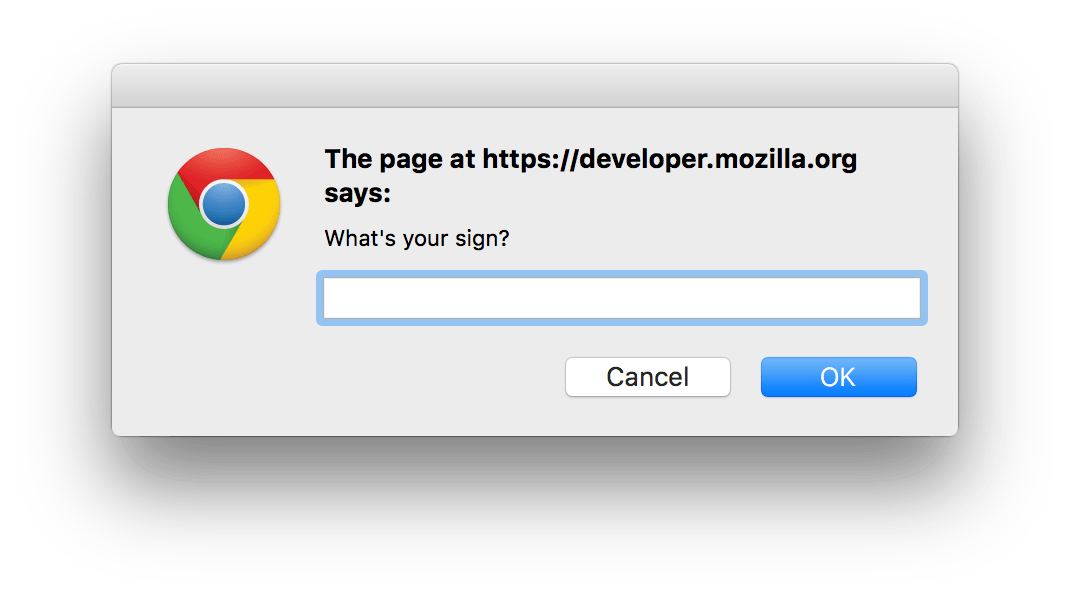
A prompt dialog contains a single-line textbox, a Cancel button, and an OK button, and returns the (possibly empty) text the user entered into that textbox.
Please note that result is a string. That means you should sometimes cast the value given by the user. For example, if their answer should be a Number, you should cast the value to Number.
const aNumber = Number(window.prompt("Type a number", ""));window.confirm()
window.confirm() instructs the browser to display a dialog with an optional message, and to wait until the user either confirms or cancels the dialog.
Under some conditions — for example, when the user switches tabs — the browser may not actually display a dialog, or may not wait for the user to confirm or cancel the dialog.
<script>
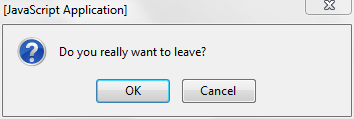
if (window.confirm("Do you really want to leave?")) {
window.open("exit.html", "Thanks for Visiting!");
}
</script>Produces:
Proper code:
<script>
alert(`enter the number`);
const a = prompt("enter here");
document.write(a);
alert(`the type of number is "${typeof a}".`);
a = Number.parseInt(a);
alert("the typeof number is " + (typeof a));
const num = prompt(`enter the number`, 47);
alert( `entered number is ${num}.`);
// document.write(num);
const write = confirm(`are you sure you want to print this number.`);
if (write) {
document.write(num);
} else {
document.write(`please allow to print the number.`);
}
</script>